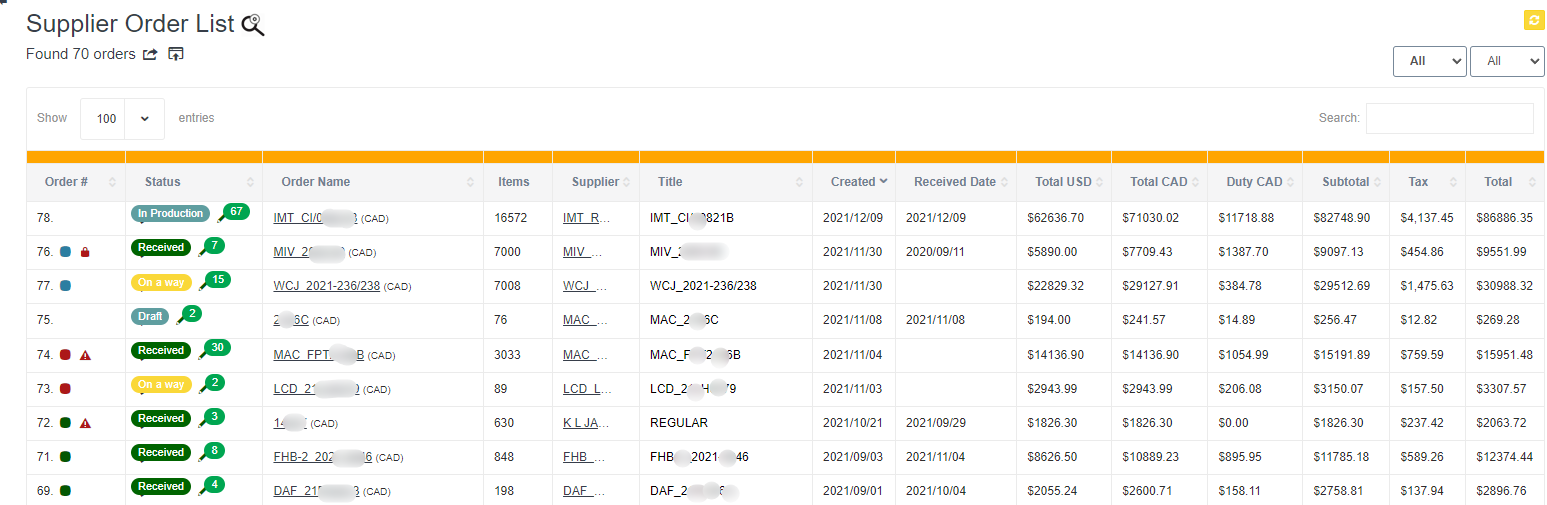
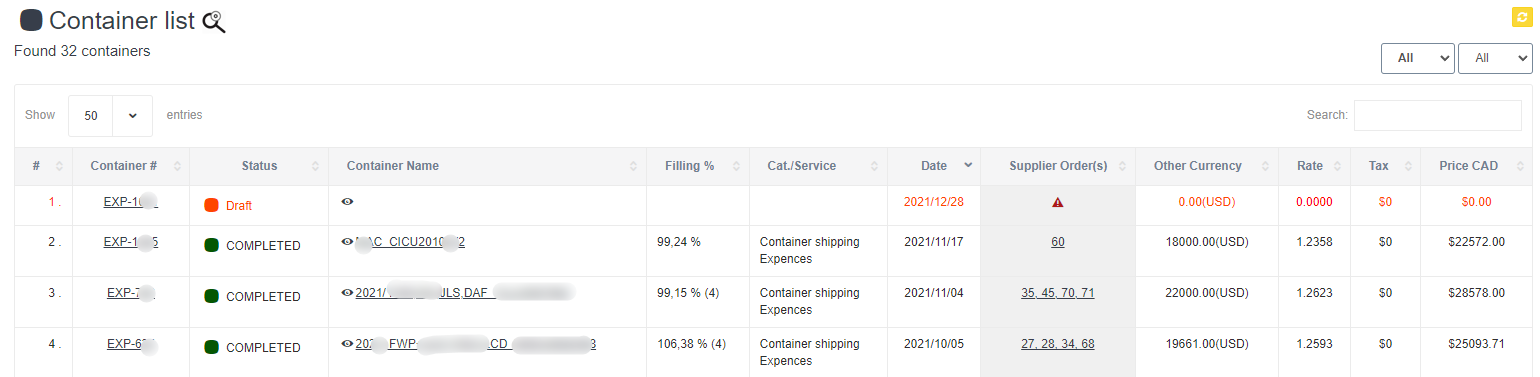
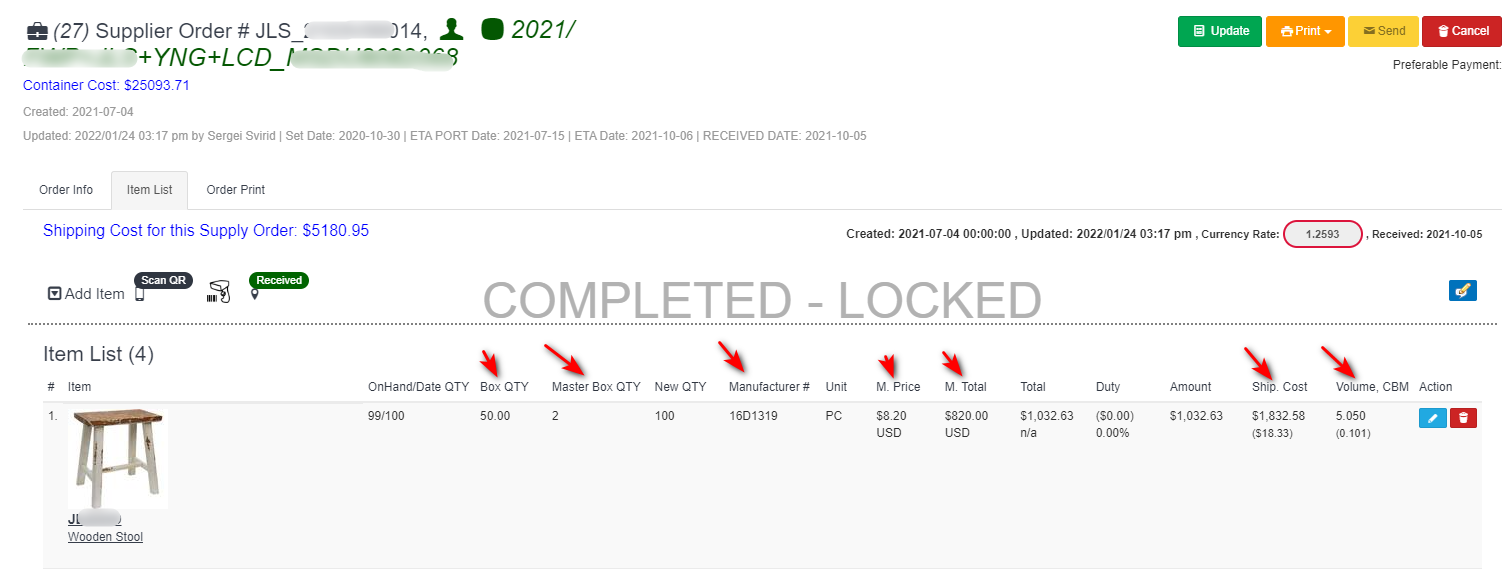
An inventory control system is a set of processes and procedures that helps businesses manage their inventory levels and keep track of their inventory movements. Here are the basic steps involved in an inventory control system:
- Receiving Inventory: When inventory is received, it should be inspected for quality and quantity. This helps ensure that the inventory meets the business’s standards and that the records accurately reflect the inventory levels. (Supply orders, Vendor orders.)
- Recording Inventory: Inventory records should be updated to reflect the receipt of new inventory. The records should include information such as the product name, quantity received, unit cost, and supplier.
- Tracking Inventory: As inventory is used or sold, the inventory records should be updated to reflect the change in inventory levels. This helps businesses keep track of their inventory levels and identify any discrepancies.
- Reordering Inventory: When inventory levels fall below a certain threshold, businesses should reorder inventory to ensure that they don’t run out of stock. The reorder point can be set based on factors such as lead time, demand, and safety stock.
- Managing Inventory Costs: Businesses need to manage their inventory costs to ensure that they are not holding too much inventory, which ties up cash flow, or too little inventory, which can lead to stockouts. This involves monitoring inventory turnover, carrying costs, and ordering costs.
- Analyzing Inventory Data: Inventory data can provide valuable insights into a business’s operations. By analyzing this data, businesses can identify trends, forecast demand, and optimize inventory levels.
Overall, an inventory control system helps businesses manage their inventory levels effectively, minimize stockouts, and optimize inventory costs.
Check our DEMO to view the Inventory system live.